Plastic forming: It is the process of using the plasticity of the material to process the parts with less cutting or no cutting under the action of external force of tools and dies. It has many types, mainly including forging, rolling, extrusion, drawing, stamping, etc.
(1) Forging

Forging: It is a processing method that uses forging machinery to apply pressure to metal billets to produce plastic deformation in order to obtain forgings with certain mechanical properties, certain shapes and sizes.
According to the forming mechanism, forging can be divided into free forging, die forging, lapping ring, special forging.
Free forging: Generally, it is the processing method to hammer the metal ingots or blocks into the required shape and size by using simple tools on the hammer forging or water press.
Die forging: It is formed by using dies on a die forging hammer or hot die forging press.
Ring lapping: refers to the production of ring-shaped parts of different diameters by special equipment ring lapping machine, also used to produce wheel-shaped parts such as automobile wheels and train wheels.
Special forging: including roll forging, wedge cross-rolling, radial forging, liquid die forging and other forging methods, these methods are more suitable for the production of certain special-shaped parts.

Process flow: forging billet heating → roll forging preparation → die forging forming → edge cutting → punching → correction → intermediate inspection → forging heat treatment → cleaning → correction → inspection
Technical characteristics:
1.the quality of forgings than castings can withstand large impact force, plasticity, toughness and other aspects of mechanical properties are also higher than castings or even higher than the rolled parts.
2、saving raw materials, but also shorten the processing time.
3、high production efficiency example.
4、 free forging is suitable for single-piece small batch production, flexibility is relatively large.
Applications:
Rollers and herringbone gears of large steel rolling mills, rotors, impellers and guard rings of turbine generator sets, working cylinders and columns of huge hydraulic presses, locomotive axles, crankshafts and connecting rods of automobiles and tractors, etc.
(2) Rolling

Rolling: the metal billet through the gap between a pair of rotating rolls (various shapes), due to the compression of the rolls forming rolling to reduce the material cross-section, the length of the pressure processing method to increase.
Rolling classification:
According to the movement of rolling parts are: longitudinal rolling, horizontal rolling, oblique rolling.
Longitudinal rolling: is the metal in two rotational direction between the rolls through, and the process of plastic deformation in between.
Cross-rolling: rolling deformation after the direction of movement and roll axis direction.
Oblique rolling: the rolled part for spiral movement, the rolled part and the roll axis non-special angle.
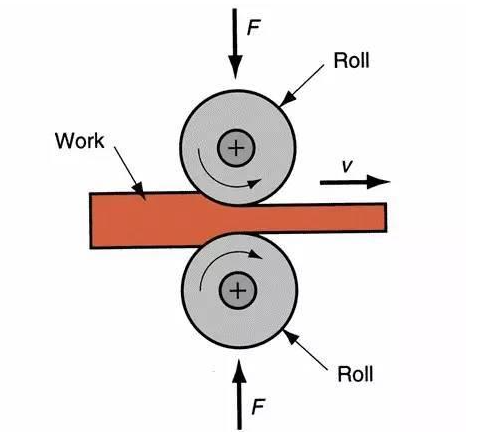
Processes:
Applications:
Mainly used in metal material profiles, plates, tubes, etc. , and some non-metal materials such as plastic products and glass products.
(3) Squeeze

Extrusion: The billet is extruded from the orifice or gap of the die under the action of uneven compressive stress in three directions so that the cross-sectional area is reduced and the length is increased to become the desired product processing method called extrusion, and this processing of the billet is called extrusion molding.
Process flow:
Pre-extrusion preparation → casting bar heating → extrusion → stretching twisting straightening → sawing (sizing) → sampling inspection → artificial aging → packaging into storage

(4) Pulling

Drawing: A plastic processing method in which a metal billet is pulled out from a die hole smaller than the billet section with an external force acting on the front end of the drawn metal to obtain a product of the corresponding shape and size.

Advantages:
1. precise dimensions and smooth surfaces;
2. simple tools and equipment;
3. Continuous high speed production of long products with small cross-sections.
Disadvantages:
1. limited amount of deformation between passes and total deformation between annealing;
2. limited length;
Production range of application: drawing is the main processing method for metal pipes, bars, profiles and wires.
(5) Stamping

Stamping: It is a forming process that relies on presses and dies to apply external forces to plates, strips, pipes and profiles to produce plastic deformation or separation to obtain workpieces (stampings) of the desired shape and size.
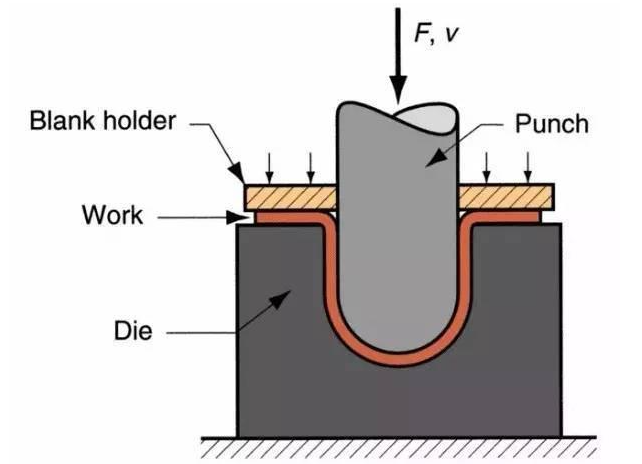
Technical features:
1、It can get light weight and high rigidity products.
2、Good productivity, suitable for mass production, low cost.
3、It can get uniform quality products.
4、High material utilization, good shearability and recyclability.
Scope of application:
60-70% of the world’s steel is plate, most of which is made into finished products after stamping. The body, chassis, fuel tank and radiator sheet of automobile, steam ladle of boiler, shell of container, silicon steel sheet of iron core of motor and electric appliance are all stamping process. There are also a large number of stamping parts in products such as instruments, household appliances, bicycles, office machinery, and living utensils.