In the last article we talked about six kinds of metal surface problems and countermeasures, let’s read on.
7.Brittleness
Defective phenomenon:
Casting base metal grains are too coarse or fine, making the casting easy to fracture or bruise.

Causes:
Overheating of the alloy solution or holding time is too long.
Intense overcooling and too fine crystallization.
Too much impurities such as zinc and iron in the aluminum alloy.
The copper content in the aluminum alloy is beyond the specified range.
The coating layer of melting tool comes off.
Analysis and judgment and solution countermeasures:
Melting furnace and temperature-controlled furnace temperature control system monitoring. The alloy should not be overheated and avoid long time insulation.
Based on mold cavity temperature field simulation analysis, find out the area with large temperature variation, add point cooling or point heating, increase mold temperature and lower pouring temperature.
Check the chemical composition of the alloy by spectral analysis. Strictly control the content of zinc and iron in the alloy.
Check the chemical composition of the alloy by spectral analysis. Strictly control the content of copper in the alloy.
Keep the molten tool coating layer intact and good.
8.Leakage & Pressure Leakage
Defective phenomenon:
Die castings are tested to produce water leakage, air leakage or water seepage. Dry pressure tester red light on

Causes:
Insufficient booster pressure.
Bad design of pouring system.
(1) Far from the leakage area and poor internal quality;
(2) Poor integration of metal flow, resulting in cold partition;
(3) Small cross-sectional area of the inner gate, inappropriate transfer of pressurization, formation of pores or shrinkage at the distal end, etc.
Improper alloy selection, poor fluidity, unsuitable for die-casting production.
Poor air venting, local defects such as porosity, shrinkage and cold compartment.
Unreasonable design of casting, uneven or over-thick wall thickness, existence of thermal junction, generating defects such as porosity, shrinkage and shrinkage cracking that seriously affect air tightness.
Large processing volume, damage the surface oxidation dense layer or make the wall thickness thinner, especially double-sided processing parts
Alloy melting temperature is too high, long holding time, easy to produce shrinkage and shrinkage crack at the wall thickness during die-casting
Large amount of coating gas, easy to produce porosity.
Pressure testing equipment failure.
The sealing surface is damaged or does not meet the roughness requirement. Such as processing surface with scratches, indentation, etc. Non-machined seal groove caused by cracking poor roughness, etc.
Warpage of sealing surface caused by deformation of casting.
Analysis and determination and solution countermeasures:
The distal end of the piece or the wall thickness is not pressed solid. Improve the specific pressure.
Can be based on simulation filling or actual sample debugging analysis and judgment. Reasonable improvement of pouring system.
Select good alloy.
Analyze whether the casting has local air rolls and poor alloy flow integration in the hot mold stage. Reasonable additional slag collection bag and exhaust channel.
Use X-light inspection to find out the hot junction. If the hot junction is indeed a leakage point, the structure can be changed and the wall thickness can be reduced in consultation with the customer’s engineer. Alternatively, a secondary extrusion process can be used to solve the leakage at the pyrolysis.
Avoid machining or use the smallest possible machining allowance.
Check the internal quality of the casting by X-ray inspection. Reduce the melting temperature appropriately.
X-ray inspection of the internal quality of the casting. Use coatings with low gas generation.
Impregnation treatment of castings.
Use qualified castings to identify pressure test equipment. Repair inspection equipment.
Can be found by pressure testing. Strengthen process protection and repair the mold in time.
Flatness inspection can be found. Control the production process, holding pressure time must be sufficient. Prevent squeezing, pressing, dropping, etc. during the process operation.
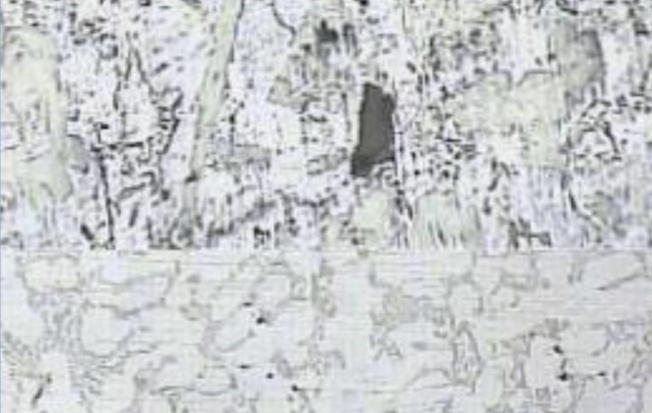
9.Pinhole phenomenon A
Defect phenomenon:
There are tiny holes inside the die casting, in many cases appearing in pieces, which are not easily detected by X-ray inspection and can only be seen on the machined surface.
Causes:
The furnace charge is not clean, with impurities containing gas, especially the use of return material.
Melting temperature is too high, resulting in the alloy liquid absorbing gas.
The alloy liquid after refining and degassing is kept for too long.
The gas product of air or lubricant enters the metal when the bulk flow is filled.
Precipitation of gas during metal melting.
Poor venting effect of mold cavity.
The mold temperature is too high and the condensation rate of alloy liquid after filling is slow.
The state of alloy flow filling is unreasonable, forming turbulent flow, so that gas enters the alloy.
Analysis and judgment and solution countermeasures:
Use clean and clean furnace material. For the return material and scrap parts, it must be graded and used, and the unqualified material should be treated before use.
Look at the melting furnace temperature control display table; must make the melting temperature control process requirements within the range.
The processed alloy liquid should be used in time as much as possible, and should not be left in the melting furnace or holding furnace for too long. The alloy liquid stored for a long time must be reprocessed before use.
Increase the speed of the metal flow as much as possible when filling the bulk flow. Reduce the diameter of the pressure chamber, reduce the cross-sectional area of the inner gate or increase the pressure injection speed.
Analyze the gas content in the metal liquid by density tester. Refine reasonably in the melting furnace and degas thoroughly after discharge.
Increase the cross-sectional area of the exhaust tank and set up the overflow tank around the casting reasonably.
Reasonable design of mold cooling system to increase the solidification speed of alloy liquid through the cooling of the whole mold.
Reasonable design of the location, direction and cross-sectional area of the internal gate to ensure continuous filling and sequential solidification of the metal flow.
10.Pinhole phenomenon B
Defect phenomenon:
The casting shows loose and uncompact macrostructure on the surface. There is an internal area of material incompatibility, accompanied by shrinkage.
It can be detected by X-ray inspection but it is somewhat blurred.

Causes:
Large alloy shrinkage, mostly in thick parts, i.e. excessive alloy volume shrinkage.
There is a sharp transition on the casting, such as a direct transition from the thin wall to the thick deep cavity, and the transition rounding is small.
Insufficient pressurization pressure.
The die-casting machine boosting pressure is established late, holding pressure time is short or can not hold pressure.
The temperature of the mold cavity is too high.
The amount of alloy liquid pouring is too little, i.e. the material cake is too thin, and the booster pressure cannot be conducted.
Too much paint spraying.
Low alloy pouring temperature
Analysis and judgment and solution countermeasures:
Change the alloy grade if possible. Reduce the thick parts of the casting as much as possible.
Adjust the structure of the casting, the transition must be rounded at the drastic change.
The surface of the casting can be found that the pressure does not achieve the image. Increase the pressurization pressure.
Overhaul the die casting machine to ensure the pressurization.
Use temperature measuring gun to detect the temperature of each part of the mold cavity. Overall mold balance set point cooling and line cooling. Spray more local high temperature areas for forced cooling.
Adopt quantitative pouring. The material cake must be controlled in the range specified by the process.
Coating is uniform and thin.
Increase the alloy pouring temperature appropriately.
11.Up mold
Defective phenomenon:
When the mold is opened after the completion of the injection process, a certain thickness of flying edge is produced on the parting surface (non-cavity part), which directly
directly affect the size of the casting. Sometimes the flying edge in the liquid state is directly spilled from the parting surface or sliding joint during the injection process.
splash out from the parting surface or the sliding joint.

Causes:
Before closing the mold, the mold parting surface is not clean, sticky with residual aluminum or other adhesions.
The moving and fixed die is not tight when adjusting the mold clamping, and the gap is large.
Die-casting machine clamping force is not enough.
Die casting mold moving, static mold surface is not parallel.
Die-casting machine 4 clamping bar stress is uneven.
The pressure of die-casting is very large and seriously exceeds the range of process requirements.
Sliding splice block gap becomes large.
The side extraction slider latching fails to work, causing the slider to back off.
The die-casting machine installation mold type plate is not parallel, which may be the problem of the type plate itself or the gap between the big bar and the guide bush is too large.
The ratio pressure of die casting becomes large, may replace the material cup with small diameter or suddenly increase in the night of die casting.
Analysis and judgment and solution countermeasures:
Check the mold parting surface, up mold state is not four directions. Clear any adhesions on the parting surface to ensure that the parting surface is clean before the mold is closed.
Check the state of the mold when the mold is closed, the state of the mold is more uniform in four directions. In the case of clean parting surface, adjust the mold closing forward.
Through theoretical calculation plus a certain insurance factor, you can find out whether the die-casting equipment clamping force is appropriate, up the state of the mold is basically four-way uniform. Replace the die-casting equipment with large tonnage. Under the premise of ensuring product quality, reduce the area of the casting row system.
In the case of ensuring the mold parting surface clean, clean, coloring with research mold (in the die-casting machine), usually is the parting surface of the local is not colored or coloring is light. Remove the mold and use the platform and height ruler to check the parallelism of the moving and static mold surface. If the parallelism is not qualified, repair the mold.
In the case of the inspection work in Article 4, if the parallelism of the mold check is qualified, consider adjusting the stress situation of the die-casting machine big bar.
Check the equipment pressure gauge of the press injection, the state of the rising mold is basically uniform in all directions. Reduce the pressure of press injection.
Sliding splice fit at the clean case, check its clearance with a stopper. Replace or repair the inserts.
With the side draw mating place cleaned up, coloring the research mating. Repair or replace the blocking fast.
Firstly, confirm that the mold moving and static handle die plane is parallel, secondly, confirm that the stress of 4 big bars is even, and the aluminum may run from one side or one corner when die-casting, producing a rise in the mold. Repair equipment.
The state of up mold is four sides evenly appear larger flying edge. Replace will raw material cup, use large tonnage die-casting machine. Keep the pressure of die-casting stable.
12.Chemical composition does not meet the requirements
Defective phenomenon:
After photoelectric spectroscopy and metallurgical microscope analysis, the casting alloy elements do not meet the requirements or there are too many impurities.
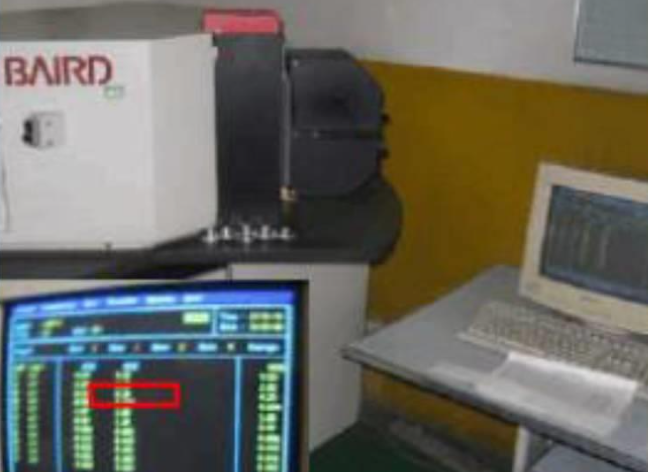

Causes:
The alloy ingot or raw material has unqualified or inaccurate composition at the factory.
The ingot or raw material has many impurities in metallographic analysis.
The returned material is not processed and analyzed and put into use, the proportion of adding too much.
The sample is not extracted or processed in the right way.
Improper melting process, such as too high temperature, serious burnout, resulting in changes in the content of certain alloying elements.
The alloy holding time is too long or the alloy liquid in the lower half of the holding furnace is not cleared as required, resulting in deposition to make the casting produce inclusions. In addition, it can also cause a change in the content of certain alloying elements.
The melting tool is not painted or the paint is peeling off.
Analysis and judgment and solution countermeasures:
Alloy ingot and raw materials into the factory before the spectral inspection. Return to the supplying manufacturer;
Metallographic examination of alloy ingots and raw materials before entering the plant. Return to the supplier;
X-light flaw detection or fracture analysis. Strict compliance with the regulations governing the use of retort materials;
Strictly implement the operation method of specimen selection and correct polishing of the surface to be examined. Take samples again for re-inspection if necessary. Conducting regular processability tests on castings during production;
Conduct photoelectric spectral analysis and metallographic examination in a timely manner. Strictly control the alloy melting temperature and pouring temperature, and try to eliminate various factors for the formation of oxides in the alloy;
Timely furnace emptying and furnace cleaning according to the process requirements;
Strictly implement the operating procedures for the use of melting tools.
13.Mechanical properties do not meet the requirements
Defective phenomenon:
The strength, hardness and elongation of the casting alloy do not meet the standard. Mainly reflected in the processing and assembly use

Causes:
Alloy chemical composition does not match the standard.
Low hardness: Low Si, Cu, Ni and Zn content.
Low strength: Low Si, Ni, Mn and Cr content.
Poor toughness: High content of Si, Mg and Zn.
Poor cutting performance: low Si, Cu, Ca content.
Casting defects such as porosity, shrinkage, slag and sparse inside the casting.
Incorrect treatment of specimens.
The casting structure is unreasonable, which limits the casting to meet the standard.
Improper melting process, producing oxides and other compounds.
Analysis and judgment and solution countermeasures:
Dosing melting to strictly control the chemical composition, so that it is within the standard requirements, preferably close to the median value.
Strictly comply with the melting and die-casting process to avoid and reduce internal defects.
Make test samples as required, and conduct regular processability tests on castings in production.
Improve the structure of the casting, avoid internal stress concentration as far as possible, and ensure round and smooth transition.
Strictly control the alloy melting temperature and pouring temperature, and try to eliminate the various factors of alloy formation of oxides.